Artificial Intelligence (AI) and robotics are rapidly transforming industries, sparking both excitement and fear about the future of jobs. Many people wonder if robots will eventually replace human workers entirely. While AI is undoubtedly reshaping the workforce, it’s crucial to look at the facts and understand the potential impacts over the next 20 years. This blog delves into the major trends, real-world data, and predictions on the future of jobs in the AI age, providing insights on which sectors may see job losses and which may thrive.
1. The Current State of AI in the Workforce
AI is already a significant player in industries like manufacturing, retail, healthcare, and finance. According to a 2023 McKinsey Global Institute report, automation could displace between 400 million and 800 million jobs globally by 2030. While these numbers may sound alarming, it’s also essential to note that AI is expected to create new jobs, particularly in tech, engineering, and AI maintenance.

- Job Automation: Routine tasks like data entry, assembly line work, and customer support are increasingly being automated. For example, companies like Amazon and Foxconn have introduced robots that can sort, package, and deliver goods. These robots operate 24/7 and can perform repetitive tasks more efficiently than humans.
- AI and Chatbots: In customer service, AI-driven chatbots like Zendesk and LivePerson are replacing human agents for handling basic inquiries. However, more complex interactions still require human input.
2. Industries Most Affected by AI
Several industries are expected to see profound changes due to AI and robotics by 2040. Here are some sectors likely to be most impacted:
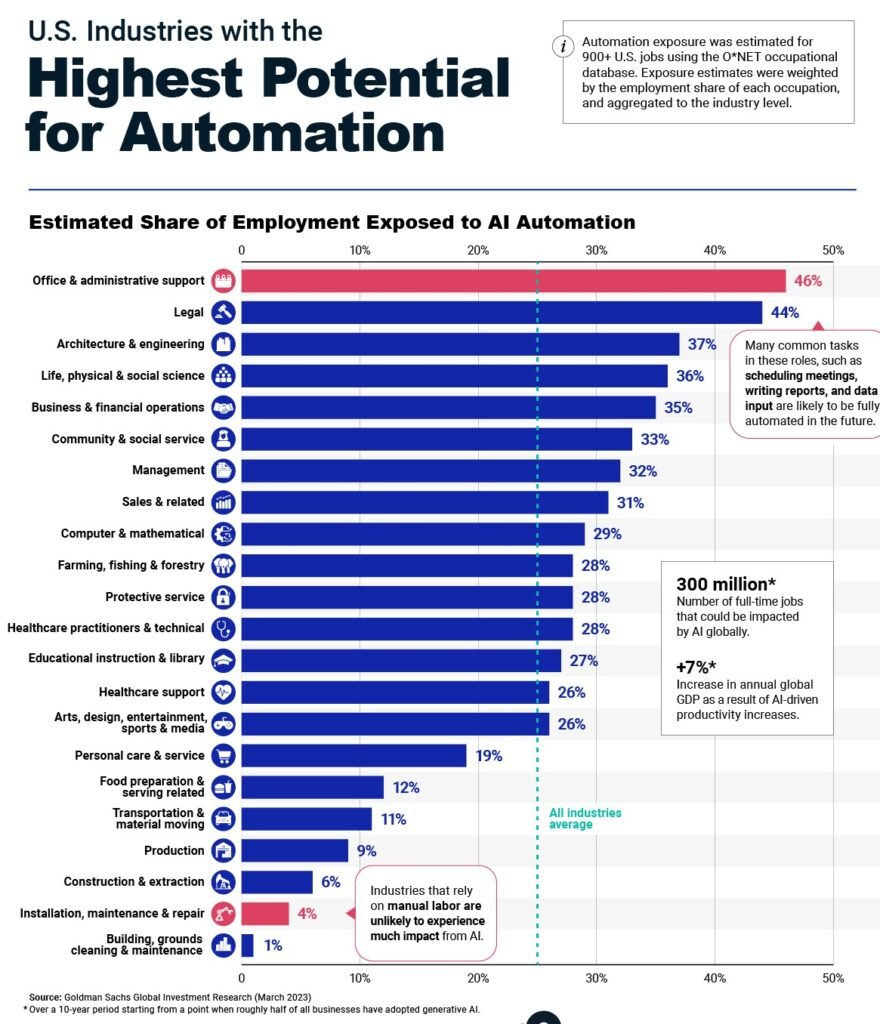
- Manufacturing: Robots are already heavily used in car production, and this trend will continue. By 2040, up to 60% of manufacturing jobs may be automated. According to a study by Oxford Economics, every new robot could replace 1.6 manufacturing jobs.
- Transportation and Logistics: Self-driving vehicles and drones are rapidly advancing. Companies like Tesla and Google’s Waymo are testing autonomous cars, while Amazon is developing drone delivery systems. The World Economic Forum predicts that driverless trucks could eliminate up to 2 million jobs in the U.S. trucking industry by 2030.
- Retail: With the rise of AI-powered self-checkout systems and e-commerce giants like Alibaba and Amazon, traditional retail jobs may continue to decline. According to Forrester Research, up to 40% of retail jobs could be at risk from automation by 2040.
- Healthcare: AI is increasingly used for diagnostics, medical imaging, and even robotic surgery. A 2020 report by PwC noted that AI could displace administrative roles in healthcare but will also create new roles in AI-driven medical services.
3. Jobs That AI Will Likely Create
Despite concerns about job losses, AI is also expected to generate millions of new jobs. In fact, The World Economic Forum predicts that AI will create a net gain of 12 million jobs by 2025. These new roles will often require specialized skills.

- AI Development and Maintenance: As AI systems become more widespread, there will be a growing demand for professionals who can build, maintain, and improve AI technologies. Jobs like AI software developers, machine learning engineers, and data scientists are expected to be in high demand.
- Cybersecurity: With the increased use of AI comes the need for better cybersecurity. AI can help identify and stop cyber threats faster than humans, but cybersecurity experts will still be essential for managing and defending AI systems.
- Human-AI Collaboration Roles: AI can enhance human productivity, creating jobs that blend human creativity with AI’s computational power. For instance, jobs in fields like digital marketing, content creation, and product design may evolve to include AI-powered tools, enabling workers to be more efficient and innovative.
- Healthcare Support Roles: While AI may automate diagnostics, the healthcare sector is likely to see more jobs in patient care, robotics-assisted surgeries, and AI-based medical innovations.
4. The Importance of Reskilling and Lifelong Learning
As automation takes over routine tasks, workers must adapt by learning new skills. Governments and companies are recognizing the need for reskilling programs to prepare workers for the future of AI-driven jobs. The International Labour Organization (ILO) predicts that by 2040, more than half of the workforce will need to reskill to remain relevant in the job market.

- Tech Skills: Learning to work with AI systems, understanding data science, and developing coding skills will be crucial for many roles. Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udacity already offer AI-related courses to help workers reskill.
- Soft Skills: AI is not good at everything. Creativity, emotional intelligence, leadership, and communication are areas where humans still outperform AI. Jobs requiring these soft skills are likely to grow, as AI complements rather than replaces human workers.
5. Will AI Completely Replace Humans in the Workplace?
One of the most pressing questions is whether AI will ever completely take over human jobs. Experts agree that while AI will automate many tasks, it is unlikely to fully replace humans, especially in areas that require emotional intelligence, creative problem-solving, and complex decision-making.

- Human-AI Collaboration: The future workplace will likely be one of human-AI collaboration, where machines handle repetitive or dangerous tasks while humans focus on creative and strategic roles. A 2022 study by Accenture found that companies combining AI with human workers saw a 20% increase in productivity.
- Ethical and Regulatory Concerns: Governments and organizations are already considering ethical frameworks to manage the rise of AI in the workforce. In the European Union, regulations like the AI Act aim to ensure that AI systems are used ethically and do not infringe on human rights. This regulatory approach will likely slow down full automation in certain sectors.
6. Challenges and Opportunities Ahead
While the future of work with AI presents significant challenges, including job displacement and inequality, it also offers substantial opportunities for growth and innovation.

- Job Polarization: Some experts warn of increased job polarization, where high-skill, high-paying jobs and low-skill jobs grow, but middle-skill jobs shrink. A MIT study noted that by 2035, 47% of jobs in sectors like manufacturing, retail, and administrative services could disappear, but there will be a growing demand for highly skilled tech and creative roles.
- Opportunities for Entrepreneurship: AI will lower the cost of entry for businesses by automating administrative tasks, enabling more individuals to become entrepreneurs. Startups utilizing AI for niche applications, from personalized learning to AI-driven marketing, are expected to flourish in the coming years.
Conclusion: Will Robots Take Over?
While AI and robotics will transform the job market over the next 20 years, it is unlikely that robots will “take over” in the sense of replacing all human workers. The future of jobs will be marked by a dynamic shift in the types of roles available, with AI automating many routine tasks but creating new opportunities in tech, healthcare, cybersecurity, and more. For workers, the key to thriving in this new landscape will be adaptability, continuous learning, and the development of skills that complement AI rather than compete with it.
